The Muscles
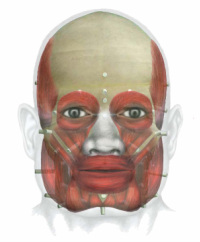
The facial muscles detailed below are the main muscles used in facial reconstruction. The facial muscles can be divided into two groups: the muscles of mastication and the muscles of facial expression. The muscles of mastication are the ones we use when we chew. The muscles of facial expression are the ones we use when we smile, laugh, or when we're sad or angry. As well as their action, the origin and insertion of each muscle is discussed. The origin of a muscle is usually where the muscle is attached to a stationary bone, while the insertion is usually it's attachment to a more moveable area. When the muscle contracts (i.e. the muscle tenses and becomes shorter), the area of insertion will generally move towards the origin.
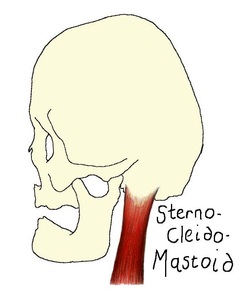
Sternocleidomastoid
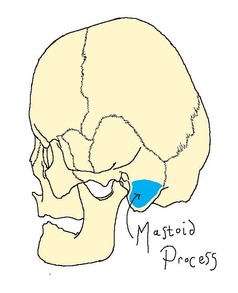
The sternocleidomastoid (SCM) originates at two heads: the sternum and the clavicle. These two heads ascend and blend to form one thick rope-like muscle which inserts at the mastoid process of the temporal bone. When both SCM muscles contract the head is tilted. When only one SCM muscle contracts the head is rotated to the side opposite the contracting muscle.
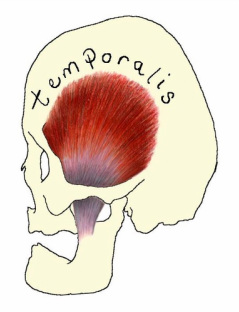
Temporalis
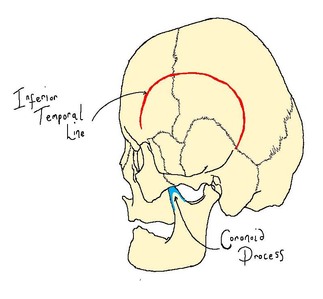
The temporalis muscle is one of the 4 muscles of mastication (so called as they are involved in the process of chewing). This is a fan-shaped muscle that originates at the inferior temporal line and passes behind the zygomatic arch to insert at the coronoid process and anterior sruface of the ramus of the mandible. When the entire muscle contracts the lower jaw is raised closing the jaw. When only the posterior portion contracts, the lower jaw is moved backwards.
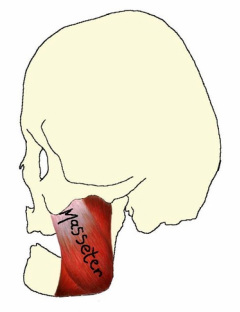
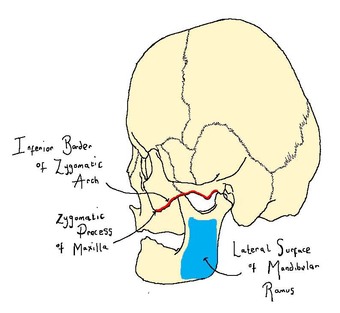
Masseter
The masseter muscle is the strongest muscle of mastication. This muscle originates at the zygomatic process of the maxilla and the lower border of the zygomatic arch, and can be seen to curve gently to insert at the lateral surface of the mandibular ramus. Bilateral contraction of this muscle will lift the mandible and close the jaw.
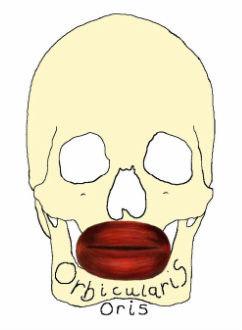
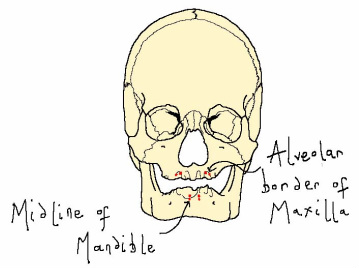
Orbicularis Oris
The orbicularis oris muscle is a circular muscle formed by muscle fibres which encircle the mouth and converge with other muscle fibres at the corner of the mouth, known as the modiolus. This muscle closes and purses the lips, compresses the lips against the teeth and aids in speech by shaping the lips.
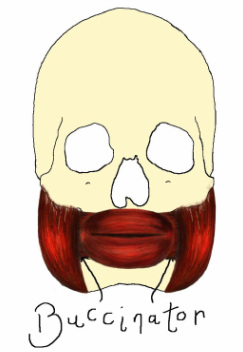
Buccinator
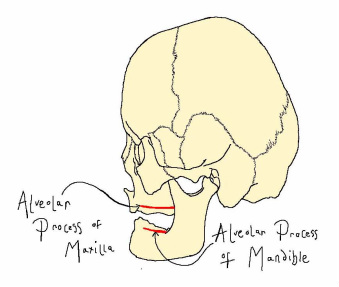
The buccinator muscle is a quadrilateral muscle which orignates at the alveloar processes of the upper and lower jaw and inserts at the modiolus. This is the muscle used when whistling or sucking and also aids in chewing by keeping food between the teeth.
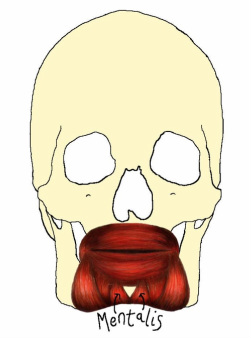
Mentalis
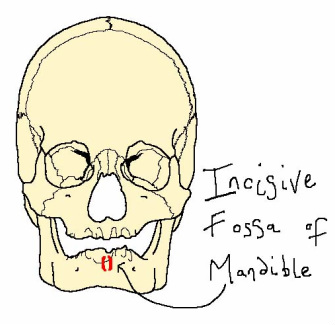
The mentalis muscle is a conical-shaped muscle which arises from the incisive fossa of the mandible and inserts at the skin of the chin. This muscle is used when pouting by lifting the chin and protruding the lower lip.
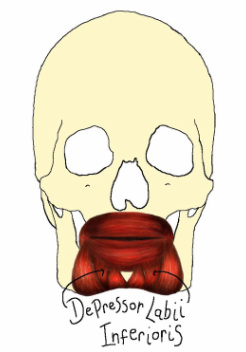
Depressor Labii Inferioris
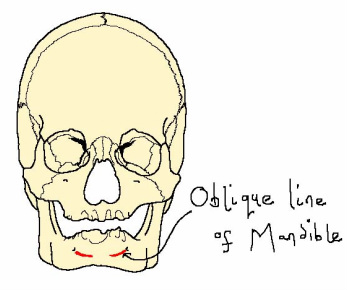
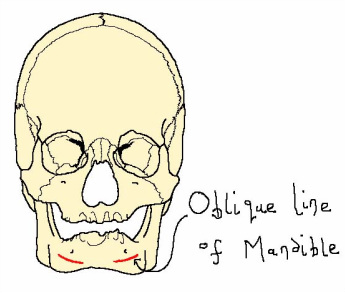
The depressor labii inferioris is a quadrilateral muscle that originates at the oblique line of the mandible and inserts at the skin of the lower lip. This muscle lowers the lower lip.
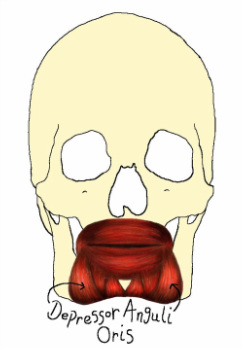
Depressor Anguli Oris
The depressor anguli oris is a fan-shaped muscle that also originates at the oblique line of the mandible but inserts at the modiolus. This muscle works by drawing the angle of the mouth either sideways or downwards creating the frowning expression.
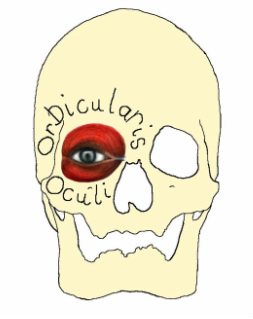
Orbicularis Oculi
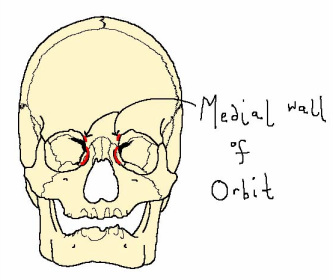
The orbicularis oculi muscle is a circular muscle that originates at the medial wall of the orbit and encircles the eye. The action of this muscle is to close the eye.
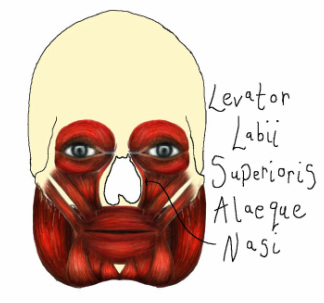
Levator Labii Superioris Alaeque Nasi (LLSAN)
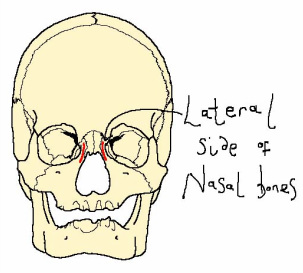
The LLSAN muscle is a thin, strap-like muscle that originates at the lateral side of the nasal bones and has two insertions: the medial branch inserts at the alae and nasal skin, while the lateral branch inserts at the upper lip. This muscle lifts the upper lip creating a sneering expression.
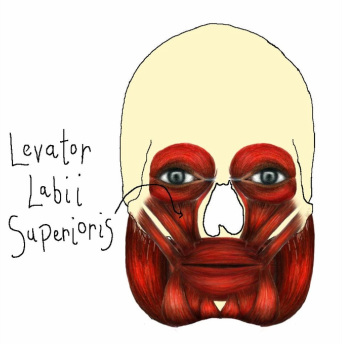
Levator Labii Superioris
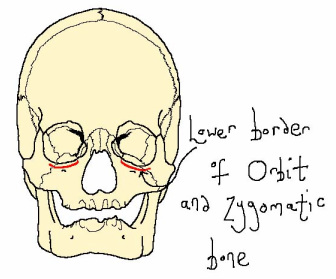
The levator labii superioris muscle is a fan-shaped muscle that originates at the lower border of the orbit and zygomatic bone, and inserts at the upper lip. This muscle works by raising the upper lip.
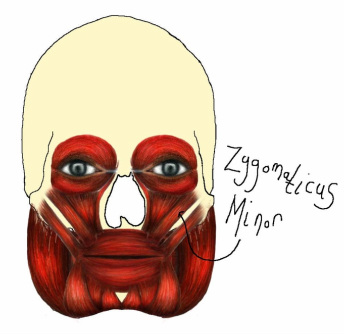
Zygomaticus Minor
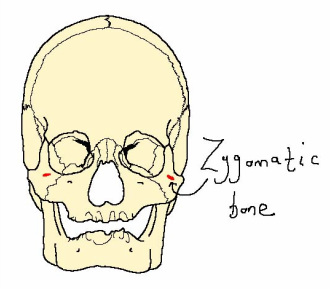
The zygomaticus minor muscle originates at the zygomatic bone and inserts at the upper lip. As one of the smiling muscles, this muscle in action will raise the upper lip to expose the maxillary teeth.
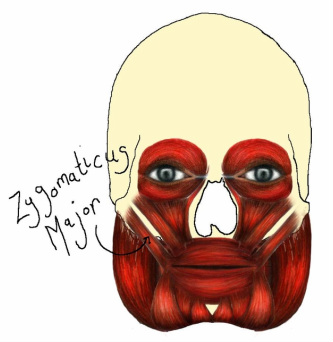
Zygomaticus Major
The zygomaticus major muscle is a strap-like muscle that originates at the zygomatic bone and inserts at the modiolus. This muscle creates a smiling expression by lifting the upper lip and drawing it to the side.
References
Feher, G. (2006) Human Anatomy for Artists. Konemann.
Grabowski, T. (2003) Principles of Anatomy and Physiology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Wilkinson, CM. (2004) Forensic Facial Reconstruction. Cambridge University Press.
Illustrations by Adrienne Barker
Grabowski, T. (2003) Principles of Anatomy and Physiology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
Wilkinson, CM. (2004) Forensic Facial Reconstruction. Cambridge University Press.
Illustrations by Adrienne Barker